This article describes the structure of a sql_handle and shows how the batch text hash component is calculated.
About This Blog
Sunday, 11 October 2020
sql_handle and the SQL Server batch text hash
Thursday, 8 October 2020
Closest Match with Sort Rewinds
In When Do SQL Server Sorts Rewind? I described how most sorts can only rewind when they contain at most one row. The exception is in-memory sorts, which can rewind at most 500 rows and 16KB of data.
These are certainly tight restrictions, but we can still make use of them on occasion.
To illustrate, I am going reuse a demo Itzik Ben-Gan provided in part one of his Closest Match series, specifically solution 2 (modified value range and indexing).
As Itzik’s title suggests, the task is to find the closest match for a value in one table in a second table.
As Itzik describes it:
The challenge is to match to each row from T1 the row from T2 where the absolute difference between T2.
valand T1.valis the lowest. In case of ties (multiple matching rows in T2), match the top row based onvalascending,keycolascending order.That is, the row with the lowest value in the
valcolumn, and if you still have ties, the row with the lowestkeycolvalue. The tiebreaker is used to guarantee determinism.
Tuesday, 4 August 2020
SQL Server 2019 Aggregate Splitting
The SQL Server 2019 query optimizer has a new trick available to improve the performance of large aggregations. The new exploration abilities are encoded in two new closely-related optimizer rules:
GbAggSplitToRangesSelOnGbAggSplitToRanges
The extended event query_optimizer_batch_mode_agg_split is provided to track when this new optimization is considered. The description of this event is:
Occurs when the query optimizer detects batch mode aggregation is likely to spill and tries to split it into multiple smaller aggregations.
Other than that, this new feature hasn’t been documented yet. This article is intended to help fill that gap.
Sunday, 26 July 2020
A bug with Halloween Protection and the OUTPUT Clause
Background
The OUTPUT clause can be used to return results from an INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, or MERGE statement. The data can be returned to the client, inserted to a table, or both.
There are two ways to add OUTPUT data to a table:
- Using
OUTPUT INTO - With an outer
INSERTstatement.
For example:
-- Test table
DECLARE @Target table
(
id integer IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL,
c1 integer NULL
);
-- Holds rows from the OUTPUT clause
DECLARE @Output table
(
id integer NOT NULL,
c1 integer NULL
);
Sunday, 5 July 2020
How MAXDOP Really Works
A few days ago I ran a Twitter poll:

The most popular answer gets highlighted by Twitter at the end of the poll, but as with many things on social media, that doesn’t mean it is correct:
Sunday, 31 May 2020
Pulling Group By Above a Join
One of the transformations available to the SQL Server query optimizer is pulling a logical Group By (and any associated aggregates) above a Join.
Visually, this means transforming a tree of logical operations from:
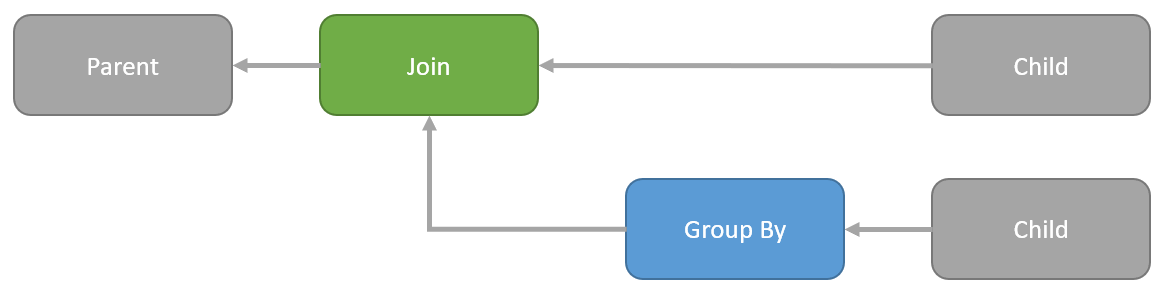
…to this:
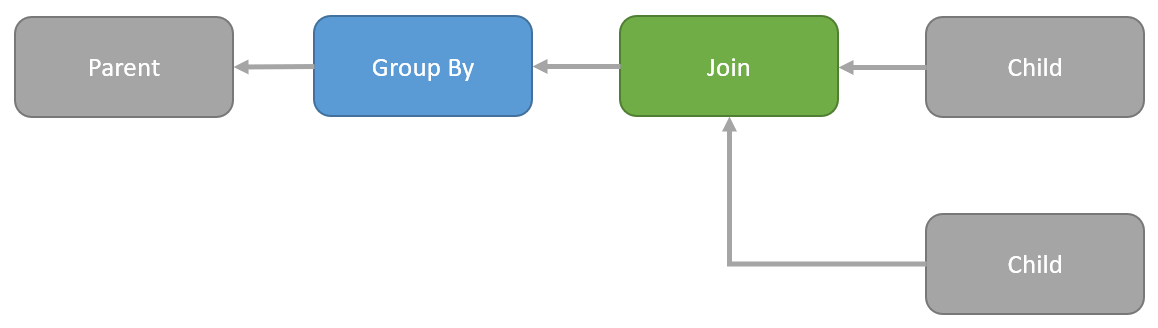
The above diagrams are logical representations. They need to be implemented as physical operators to appear in an execution plan. The options are:
- Group By
- Hash Match Aggregate
- Stream Aggregate
- Distinct Sort
- Join
- Nested Loops Join
- Nested Loops Apply
- Hash Match Join
- Merge Join
When the optimizer moves a Group By above a Join it has to preserve the semantics. The new sequence of operations must be guaranteed to return the same results as the original in all possible circumstances.
One cannot just pick up a Group By and arbitrarily move it around the query tree without risking incorrect results.